In psychology, self-concept or self-perception, is how you understand and see yourself. It is a self-evaluation that embodies the answer to the question, “Who am I?” Self-concept includes how you perceive your behavior, abilities, characteristics, and values. Developed from childhood, it shapes our thoughts, feelings and how we interact with the world. It molds our future identity. Self-concept changes over time, influenced by your surroundings, your achievements, and your evolution as a person. How good or bad your self-concept is crucial to your self-esteem and mental health.
According to social psychologist Roy Baumeister, self-concept is like a knowledge structure in which people pay attention to their internal and external behavior. This self-awareness enables us to gain insight into ourselves. Self-concept is then developed from this information and continues to grow as people discover themselves.
Why Self-concept matters
Self-concept matters because it influences our motivations, attitudes, and behavior. It gets us thinking, are we competent enough? Or how much is our self-worth? Self-concept is multidimensional, and shaped over time by every aspect of our lives, from how we behave with others to society and culture at large. Self-concept is easily molded at a younger age when we are still going through phases of self-discovery and identity. As we age and learn who we are and what’s important to us, our self-concept will become more evident, detailed and organized.
Examples of Self-Concept Include:
- “I am an excellent teacher.”
- “I’m an accomplished musician,”
- I’m a published author
- I’m a person who loves animals
- “I’m a successful sportsperson.”
While these are positive examples of self-concepts, a person might have other views about themselves, such as “I don’t like crowds and prefer a quiet evening” or “I’m a laid-back person.” How you see your personality defines whether you are an introvert or an extrovert. Moreover, saying “I’m a brother,” or “I’m a mother”, is a self-perceiving role in life that defines your identity. Providing an extension of who you are reinforces the belief in yourself and helps others understand more about you. The labels you attribute to yourself are the various hobbies, professions or passions that describe the kind of person you are, such as a sportsman, adventurer, or politician.
Three Components of Self-Concept
Self-concept is always different for everyone. Different dimensions of self-concept might not relate to each other. For example, the self-concept of academic proficiency will not overlap with social skills; this means someone with good academic skills may need to be more adept at social skills but are efficient nevertheless. While different dimensions of self-concept remain distinct, some characteristics are commonly agreed upon as the basic concepts and components of self-concept. It was humanist psychologist Carl Rogers who outlined three different parts of self-concept widely agreed upon as the standard components of self-concept today.
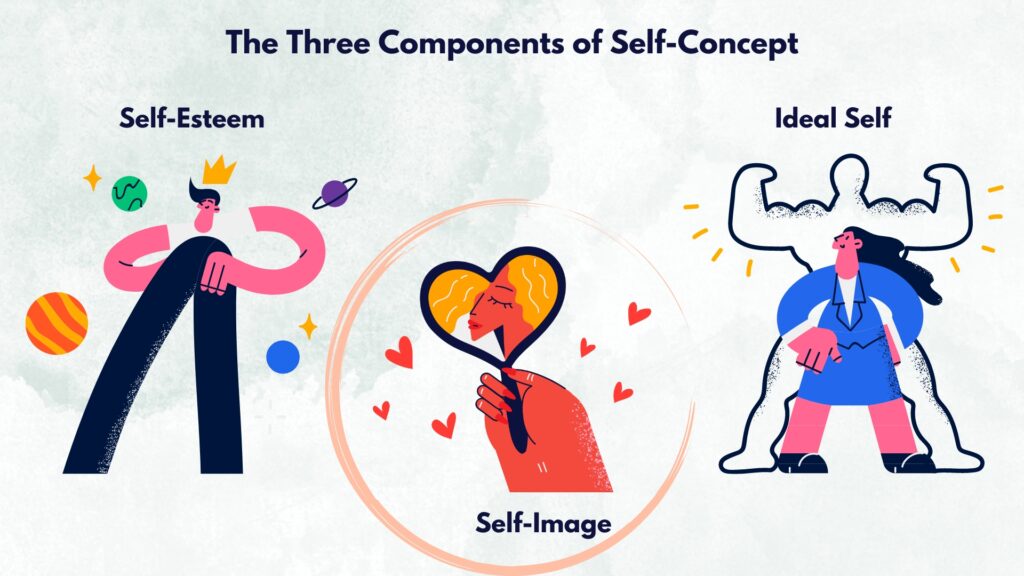
Self-Image: Self-image refers to how we see and describe ourselves. It includes the way you see your physical appearance, abilities, characteristics, and personality traits. Self-image is influenced by your self-assessment as well as feedback from others. For example, if you feel you are a confident and intelligent person, your self-image will reflect this positive quality in your behavior. However, self-image does not always reflect reality. There are some people with inflated egos and false perceptions of themselves. This exaggerated self-perception can be either a positive or negative one.
Self-Esteem: Self-esteem is self-acceptance; it is how much you value yourself. Self-esteem is influenced by how you evaluate your capabilities, comparison to others and how others respond to you. Self-esteem plays a vital role in our mental health and well-being. Those with high self-esteem, regard themselves in a more positive light, are confident and learn to accept themselves. Low self esteem on the other hand, is associated with self-doubt, low confidence, self-criticism, and a poor regard of one’s self-worth.
Self-Ideal: This represents the kind of person you want to be. It is the ideal personality with all the attributes, qualities, values, and characteristics you aspire to be. Self-ideal serves as a motivational force, it prompts us to establish challenging goals, be more efficient and strive towards self-improvement because it is exactly who we want to be.
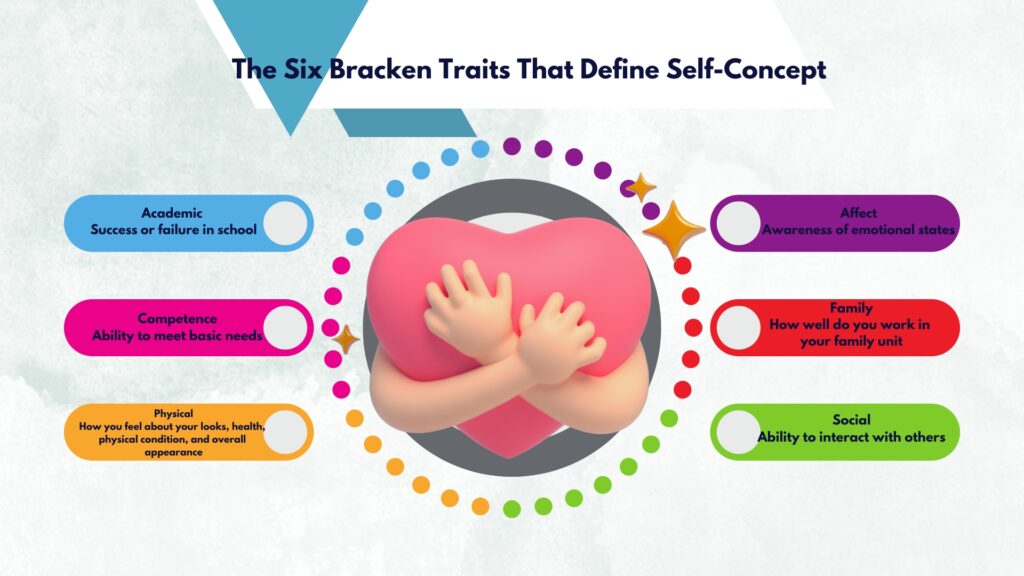
To extend on the multidimensional construct of self-concept, Psychologist Bruce A. Bracken believed that self-concept consisted of six independent traits. In 1992, Bracken even developed a comprehensive assessment tool called the multidimensional self-concept scale that evaluates these six traits in children and adolescents. The six Bracken traits of self-concept are:
- Academic: Success or failure in school
- Affect: Awareness of emotional states
- Competence: Ability to meet basic needs
- Family: How well do you work in your family unit
- Physical: How you feel about your looks, health, physical condition, and overall appearance
- Social: Ability to interact with others
How Self-Concept Develops
Self-concept develops in early childhood and evolves throughout life. However, self-concept experiences the most growth between early childhood and adolescence. It further advances as we acquire language, engage in social interactions and form relationships. Our interaction with the world, including strangers, colleagues, family, and friends, all contribute to our sense of self-concept. As children, the feedback is primarily from parents, elders, and caregivers. These, in fact, or crucial years where emotional security and positive reaffirmation contribute to high self-esteem. Alternately, criticism, neglect, and negative responses can negatively impact self-concept, which leads to the development of an insecure individual with low self-esteem.
According to one study, the progress of self-concept in high-performing students is directly impacted by how much a teacher believes in their abilities.
Growing older, our self-concept is influenced by social comparisons, cultural influences, and feedback from various sources. Understanding societal expectations, social norms, traditions, culture, and our role in social groups will then shape our self-conceptual behavior as adults. Even social media and mass media impact our sense of self-concept. When media platforms promote various ideals that individuals tend to make into their own. The more we see such ideals played out on media platforms, the stronger it affects our self-identity and self-perception.
How Self-Concept Affects Personal Growth and Development
Resilience and Coping Abilities: Positive self-concept promotes stronger resilience in facing adversity, challenges, and obstacles. If you have a positive image of yourself, you are more likely to cope better, strategize well, and bounce back from failure with more determination to succeed.
Setting goals and achievements: Self-concept influences the goal we set for ourselves. A positive self-concept supported by high self-esteem will always promote challenging goals. This works as a confidence booster in one’s abilities needed for personal success.
Healthy Relationships: Since our interaction with others influences our self-concept, it will also affect the quality of our relationships. Those with positive self-concepts end up in healthier relationships based on mutual respect, trust, and proper communication. It also helps us establish boundaries, assert what we need in relationships, and make decisions aligned with our values.
Mental Health and Well-Being: Perhaps the most important role of Self-concept, our emotional well-being is greatly impacted by the levels of self-concept. Those with positive self-concepts are likelier to be happy and content with their lives. They also possess the skills to manage stress and criticism and take the challenges and complexities of life head-on. Studies found low self-concept contributed to depression and anxiety.
Conclusion
Self-concept helps us recognize our true value and self-worth. While not self-esteem, it is how we define ourselves to increase self-esteem. When your self-concept is strong and positive, it protects you from negative criticism from others. Self-concept never ends. Because our actions and social environment always influence it, it evolves and changes. Even though self-concept is greatly molded in childhood, as an adult, with a more positive environment, and experiences, you can change your perception of yourself to a more reaffirming one.