The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders version 5 ( DSM-5) of American Psychiatric Association has put autism and other mental disorders namely Rett Syndrome, Child Disintegrative Disorder, Asperger’s Syndrome and PDD-NOS( Pervasive Developmental Disorder, Not Otherwise Specified) under the name of AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDERS or ASD and has set a criteria for mental health professionals to diagnosed ASD.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are complex neurological disorder that affects the verbal and nonverbal communication of the child, the presence of restrictive and repetitive behaviors, interests, or activities, limited social interaction and a lifelong impact on the development of various abilities and skills that directly create hurdles in their academic and social lives. The symptoms of ASD can range from mild to severe impairments in several areas of development.
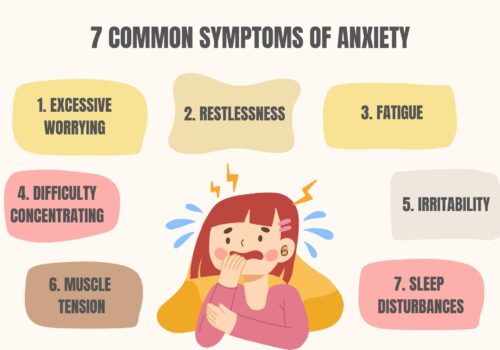
Some of the most common symptoms observed in ASD children are:
Diagnostic Symptoms
- Individuals with ASD have limited curiosity or desire to socialize with others. The mothers of ASD children may notice following symptoms in the early stages of their babies development:
- ASD children do not respond when their name being called.
- At the age of 6 months, unlike normal children, ASD children do not smile widely or make joyful expression or respond to games like peek-a-boo.
- At the age of 9 months, normal children engage in smiling, making sounds and faces but ASD children do not respond to any of these activities.
- Normally kids start babbling and making gestures like showing, pointing or waving by the age of 12 months, but ASD children lack in all those gestures and development.
- The ASD child is not aware of the group concept and does not respond to it. Like normal children, they do not run-up to play with other children. The ASD child unintentionally loves to play alone and often restricted to specific types of games and activities. They are unable or unwilling to follow basic rules of a group-play like turn-taking, role- playing or the basic rules of any sport. They engage themselves in activities that serve no purpose or meaning.
- The ASD children find it difficult to distinguish between living things and non living things which mean they can treat non living-things like a living one.
- ASD children have certain obsessions, routines and topics of conversations. For example, some children might collect strange objects like threads, combs or twigs to play. Some might open and close door again and again, some might be interested in knowing everything about trains, cars or any other thing that sound fascinating to them. Some might have favorite place to keep their toys, might drink or eat from particular mug or plate.
- ASD children when found a pleasurable experience, they then tend to repeat it endlessly as their behavior lacks variation and their interests are very limited
Non- Diagnostic Symptoms
- ASD children have unusual responses to sensory stimulation. Some may be highly sensitive towards certain sounds like, sound of bell, horn or radio or alarm clock while others may be under sensitive towards these sounds and feel distressed.
- ASD children are often fascinated by bright lights or flashing lights. Also some ASD children have obsession towards rotating objects like ceiling fan, toy cars and any rotatory objects. They can spend hours looking at them.
- ASD children have excellent photographic memory for places or things.
- ASD children have a difficulty seeing objects as a whole, for instance you could hear saying them that they had never seen a tree, just thousands of leaves and this type of visual concept difficulty can interferes with learning.
- ASD children are unduly sensitive to pressure on the skin which implies they may find obvious relief in taking tight garments off or they may seek and enjoy pressure on skin and joints. Normal people do not feel their tight socks or underwear half a minute after they wore them but the ASD children may continue to be aware of such sensations for hours.
Language and Imagination
- Language has two components namely verbal and non-verbal. Non-verbal skills include facial expression, eye contact, gesture, posture, body language, motion and paralanguage. Verbal skills include words, sentences, phrases, written text verbs, adjectives, contextual communication and active listening.
- In ASD children, non -verbal skills are poor. They may give empty gaze or discomforting gaze, their body language may be inappropriate such as they may be unaware of personal space so they may be sitting and standing too close for conversational comfort. You may find them smiling or gesturing inappropriately which is unrelated to the current situation. ASD children are unable to understand the meaning of words in their most literal sense, so they are not unable to understand sarcasm, puns and metaphor and hence not able to maintain a conversation.
- In ASD children, expressive language follows an abnormal developmental path. The child may repeats words or phrases just heard without understanding their meaning, this abnormal developmental path is known as Immediate Echolalia and sometimes child may suddenly repeat words or phrases which he/she heard a day or two before and this abnormal developmental path is known as Delayed Echolalia.
Myths About Autism Spectrum Disorder
- ASD is rare and is an emotional disorder but the fact is, it is an neurological disorder and 1 in every 165 persons has ASD.
- Poor parenting causes ASD and everyone with ASD behaves in the same way but the fact is parenting has nothing to do with the cause of ASD and ASD kids have their own strengths and weaknesses.
- There is a cure for ASD, ASD can never be cured completely but ASD children can make significant progress with early intervention.
Conclusion
ASD is a type of neurological disorder and a child is born with it. Sometimes the parents might blame themselves for their kids’ condition and have a very stressful situation, behavioral issues and the constant over thinking about the future of their child. With the early intervention and medical help along with the self awareness and positive attitude of parents, the ASD children can also live a happy life. When provided positive reinforcement by the parents and caregivers, the ASD children respond well, try a lot of different techniques and approaches to figure out what suits your child the best and stay motivated even if they do not respond well to a particular approach. ASD children love their routines, so try to be consistent on the new techniques and provide the necessary time to your child. Do not hide your child from what the world thinks and react, make them familiar with their surroundings and daily activities. Respect their choices and observe their reactions carefully, take them time to learn from experience and be patient. As a parent, loving your child for who he is and the way he is, is the key.
REFERENCES
https://www.webmd.com/brain/autism/parenting-child-with-autism