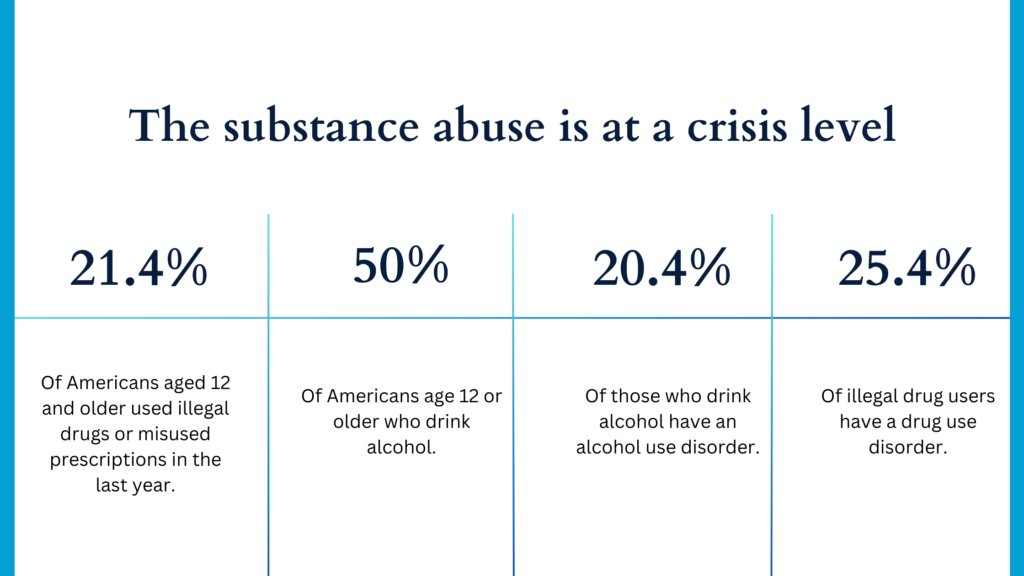
Substance use disorder is a complex and challenging condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Whether it’s alcohol, illicit drugs, prescription medication, or even certain behaviors like gambling, substance use disorder can have devastating consequences for a person’s health, relationships, and overall well-being. To effectively address this issue, it is essential to have a deep understanding of its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of substance use disorder, shedding light on its underlying causes and potential risk factors. We will explore the symptoms and behavioral patterns associated with substance abuse, enabling individuals to recognize the signs in themselves or their loved ones. Furthermore, we will discuss evidence-based treatment options, such as therapy, medication, and support groups, that can aid in the recovery process.
By improving our understanding of substance use disorder, we can contribute to breaking the stigma surrounding addiction and provide support to those in need. Join us on this enlightening journey as we explore the intricacies of substance use disorder and discover ways to promote hope, healing, and lasting recovery.
What is Substance Use Disorder?
Substance use disorder, also known as addiction, is a chronic brain disease that involves the compulsive use of substances despite negative consequences. It is characterized by a loss of control over substance use, cravings, and continued use despite harmful effects on physical and mental health. Substance use disorder can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. It is important to recognize that addiction is not a moral failing or a lack of willpower, but rather a medical condition that requires proper treatment and support. Substance use disorder can involve various substances, including alcohol, opioids, stimulants, sedatives, and hallucinogens. It can also manifest as an addiction to certain behaviors, like gambling or internet use. The use of these substances or engagement in these behaviors alters the brain’s reward system, leading to a cycle of compulsive use and cravings.
Understanding the Causes of Substance Use Disorder
The development of substance use disorder is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. While genetics can predispose individuals to addictive behaviors, environmental factors such as family history of substance abuse, peer pressure, and exposure to trauma or stressful life events also play a significant role.
Psychological factors, such as mental health disorders like depression or anxiety, can contribute to the development of substance use disorder as individuals may turn to substances as a means of self-medication. Additionally, social and economic factors, such as poverty, unemployment, and a lack of access to healthcare or support services, can further increase the risk of substance abuse.
Common Symptoms of Substance Use Disorder
Recognizing the symptoms of substance use disorder is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Some common signs and symptoms include:
1. Loss of control: Individuals with substance use disorder often find it challenging to control their substance use, despite negative consequences. They may consume larger amounts of the substance or use it for longer periods than intended.
2. Cravings: Intense cravings for the substance are a hallmark of substance use disorder. These cravings can be overwhelming and difficult to resist, leading to continued use.
3. Neglecting responsibilities: Individuals may neglect their responsibilities at work, school, or home due to their focus on obtaining and using the substance.
4. Withdrawal symptoms: When individuals abruptly stop or reduce their substance use, they may experience withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, sweating, insomnia, and irritability. These symptoms can vary depending on the substance involved.
5. Tolerance: Over time, individuals with substance use disorder may develop tolerance, requiring larger amounts of the substance to achieve the desired effect.
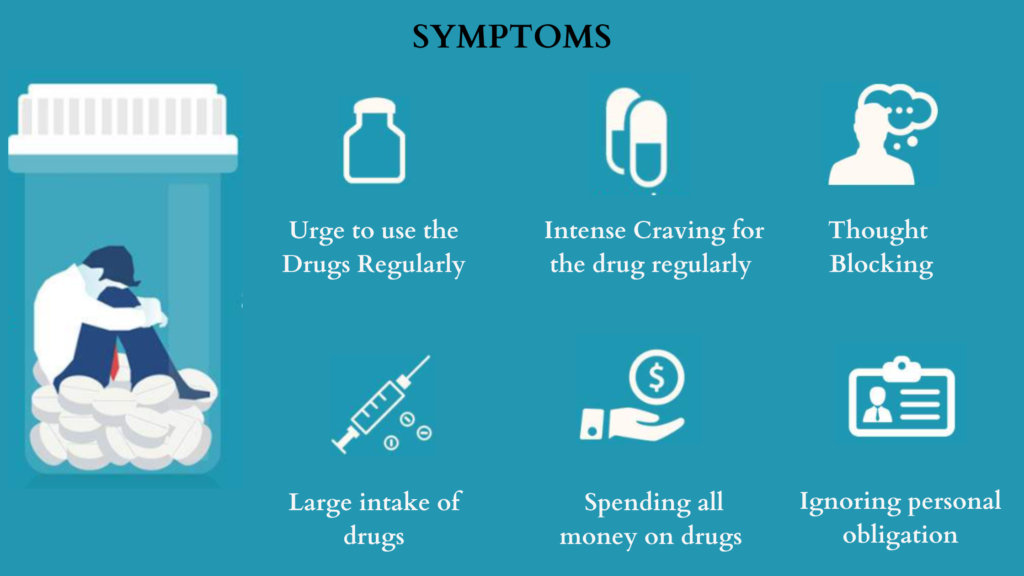
It is important to note that the presence of these symptoms alone does not necessarily indicate a substance use disorder. A comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
The Impact of Substance Use Disorder on Individuals and Society
Substance use disorder has far-reaching effects on both individuals and society as a whole. From a personal standpoint, addiction can result in severe physical and mental health problems, strained relationships, financial difficulties, and legal issues. It can also lead to isolation and a loss of self-esteem.
On a societal level, substance use disorder places a significant burden on healthcare systems, criminal justice systems, and the economy. It contributes to increased healthcare costs, productivity losses, and an increased demand for social services. The consequences of substance abuse extend beyond the individual, impacting families, communities, and society as a whole.
Different Types of Substances and Their Effects
Substance use disorder can involve various substances, each with its own set of effects and risks. Some common substances of abuse include:
1. Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and mental health disorders. It is a leading cause of accidents, injuries, and death.
2. Opioids: Opioids, including prescription painkillers and illicit drugs like heroin, can cause respiratory depression, overdose, and addiction. The opioid crisis has reached epidemic proportions in many countries.
3. Stimulants: Stimulant drugs like cocaine and methamphetamine can have severe cardiovascular and neurological effects. They can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and psychosis.
4. Sedatives: Sedative drugs, such as benzodiazepines, are commonly prescribed for anxiety and sleep disorders. Prolonged use can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
5. Hallucinogens: Hallucinogenic substances like LSD and psilocybin mushrooms can cause hallucinations, altered perceptions, and psychological distress. Each substance has its own set of risks and potential long-term effects. It is important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is struggling with substance use disorder.
Treatment Options for Substance Use Disorder
Fortunately, there are effective treatment options available for substance use disorder. Treatment approaches may vary depending on the individual’s specific needs and the substances involved. Some common treatment options include:
1. Therapy: Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing, can help individuals identify and change harmful patterns of thinking and behavior.
2. Medication-assisted treatment: Medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine for opioid use disorder, can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, enabling individuals to focus on their recovery.
3. Support groups: Support groups like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA) offer a sense of community and peer support, allowing individuals to share their experiences and learn from others in similar situations.
4. Inpatient rehabilitation: In severe cases of substance use disorder, inpatient rehabilitation programs provide a structured environment with intensive therapy and medical support.
5. Aftercare and relapse prevention: After completing treatment, individuals may benefit from ongoing support and relapse prevention strategies to help maintain their recovery. It is crucial to remember that recovery is a lifelong process, and relapse is a possibility. Continual support and treatment are essential for long-term success.
Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
One of the major barriers to seeking help for substance use disorder is the stigma associated with addiction. Society often views addiction as a moral failing or a lack of willpower, which can prevent individuals from seeking the treatment they need. Overcoming this stigma requires education and empathy.
By understanding that addiction is a medical condition and not a character flaw, we can create an environment that encourages individuals to seek help without fear of judgment or discrimination. It is important to offer support and resources to those struggling with substance use disorder, treating them with dignity and respect.
Support Systems for Individuals With Substance Use Disorder
Building a strong support system is crucial for individuals with substance use disorder. Support can come from various sources, including:
1. Family and friends: Loved ones can provide emotional support, encouragement, and understanding throughout the recovery process.
2. Therapists and counselors: Mental health professionals can offer guidance, therapy, and coping strategies to help individuals navigate the challenges of recovery.
3. Support groups: Peer support groups like SMART Recovery or Refuge Recovery provide a safe space for individuals to connect with others who have similar experiences.
4. Community resources: Local community centers, religious organizations, and nonprofit organizations often offer resources and programs to support individuals in recovery.
By surrounding themselves with a supportive network, individuals with substance use disorder can increase their chances of successful recovery and long-term sobriety.
Preventing Substance Use Disorder and Promoting Healthy Habits
Prevention plays a crucial role in addressing substance use disorder. By promoting healthy habits and addressing risk factors, we can reduce the likelihood of individuals developing addiction. Some key prevention strategies include:
1. Education: Providing accurate and evidence-based information about the risks of substance abuse can help individuals make informed choices.
2. Early intervention: Identifying and addressing risk factors, such as mental health disorders or a family history of substance abuse, at an early stage can prevent the development of addiction.
3. Promoting healthy coping mechanisms: Encouraging individuals to develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, mindfulness, or creative outlets, can reduce the likelihood of turning to substances in times of stress.
4. Reducing access to substances: Implementing policies and regulations that restrict access to substances, especially among vulnerable populations like adolescents, can help prevent substance abuse.
Conclusion
Substance use disorder is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can break the stigma surrounding addiction and provide support to those in need. Education and empathy are key to fostering understanding and compassion for individuals struggling with substance use disorders. Together, we can promote hope, healing, and lasting recovery for those affected by this challenging condition.
In conclusion, substance use disorder is a serious and widespread issue that affects individuals and society as a whole. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can work towards breaking the stigma surrounding addiction and providing the necessary support for those in need. Through education, empathy, and a comprehensive approach, we can promote hope, healing, and lasting recovery for individuals struggling with substance use disorder.