Neurodivergent means being neurologically different. Not everyone’s brain functions the same. There are some people whose brains are wired differently and feature abilities and constraints, unlike normal people. Neurodivergence is “being different” and can include conditions like ADHD, Autism, dyslexia, Savant syndrome, and Asperger’s, to name a few. Neurodivergence is not a medical disorder or a defect; it is a variation that contributes to the variety of human experience.
Neurodivergent, an Overview: What Is It?
Neurodivergent is a nonmedical term to describe people whose brains aren’t typical of the average human. Neurodivergent people may have an existing neurological conditions or one that is yet to be identified.
Earlier, neurodivergence was considered abnormal, but today, extensive research and case studies have helped scientists understand how being neurodivergent benefits an individual in many ways. Neurodivergent diversity manifests as both a potential condition and an ability, like synesthesia, where the brain gives a person simultaneous multisensory experiences. Neurodivergence affects how individuals think, process information, perceive the world, and interact with others. It does not conform to being either typical or neurotypical but deviates from all understanding of how a human brain works. It is a fascinating condition that highlights the diversity in how the human brain functions.
Understanding Neurodiversity
Neurodiversity is a term first coined in 1997 by autistic sociologist Judy Singer. Singer described how neurodiversity includes two categories: Neurotypical people and neurodivergent.
- Neurotypical: normal people with typical, standard cognitive function displaying normal behavior. Such persons achieve the usual behavioral milestones at times and ages when they are expected to without the need to question if their cognition is the same as others.
- Neurodivergent: People with unusual and different cognitive functions where there is a possibility of just one or many differences. The neurodivergence can range from mild to intense, causing those affected to behave differently from an average human.
Neurodivergence Includes a Variety of Syndromes
Since it is neither a disorder nor a defect but rather reflects a cognitive variation of the human brain, neurodivergence can hence include a variety of known conditions, such as:
- Autism spectrum disorder (once called Asperger’s syndrome)
- Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Down syndrome
- Dyscalculia (difficulty with math)
- Dysgraphia (difficulty with writing)
- Dyslexia (difficulty with reading)
- Dyspraxia (difficulty with coordination)
- Intellectual disabilities
- Bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and more
- Prader-Willi syndrome
- Sensory processing disorders
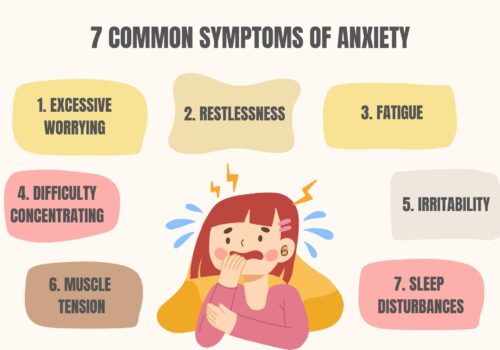
- Social anxiety
- Tourette syndrome
- Williams syndrome
Most of these conditions, like autism, come with obstacles, including some incredible abilities, like visualizing in 3D, “Doctor Shaun Murphy ring a bell?” Neurodivergent people possess uncanny abilities such as creative problem-solving, innovation, and alternative approaches to challenges. In essence, being neurodivergent celebrates and recognizes the human mind’s diversity and uniqueness. It encourages people to adopt a more flexible perspective on human experience and function rather than being fixed on a one-size-fits-all approach.
Common Neurodivergent Traits
While neurodivergence includes various conditions, there are certain specific traits unique to some or all individuals who fall under the umbrella of being neurodivergent.
- Sensory Sensitivity: A heightened or diminished sensory sensitivity with intense reactions to stimuli like light, sound, texture, or taste.
- Pattern Recognition: Some neurodivergent individuals possess extraordinary Savant skills to recognize patterns in numbers, words, and visual cues, thus making them extremely talented mathematicians, musicians, and artists. One example is the mathematical genius and Nobel prize winner John Nash, who had Schizophrenia, but it is now widely believed he also had Asperger’s or Autism. John Nash is best depicted in the Hollywood movie “A Beautiful Mind” starring Russel Crowe.
- Attention Variability: Neurodivergent individuals possess varied attention spans, where some display a sense of hyperfocus while others might struggle to be attentive to even fewer engaging activities.
- Differences in Social Interaction: Neurodivergent people might find it hard to socialize because of the inability to communicate verbally and understand social cues and norms.
- Unique Interests: Neurodivergent individuals often develop an intense interest in specific subjects or hobbies, especially when it includes their expertise and makes them happy.
Myths about Neurodiversity
Even though there is a growing awareness of neurodiversity, some myths still stigmatize the condition.
Neurodivergence is a Disability
Being neurodivergent does not necessarily mean a disability. However, some medical experts like to argue and oppose the concept of neurodiversity because those who are neurodivergent will always have a medical condition needing treatment. Neurodivergent people might struggle with challenges and systems that disallow them from displaying their true abilities. For example, a dyslexic person might find reading difficult due to their brain’s inability to process written language. On the other hand, their brains are more advanced than normal people, where processing and visualizing 3D objects are concerned. It makes them exceptionally adept at identifying optical illusions, and they will have a natural flair for jobs like graphic design, architecture, and engineering.
A One-Size-Fits-All Approach
Every individual is unique and has their own needs. It is also similar in a mental scenario because, like fingerprints, no two brains are the same. Thus, nothing can define what is normal for the human brain, which means there is also no uniform approach to accommodating neurodivergent individuals. Tailored support is essential.
- Example #1: A neurodivergent person might find a noisy working environment difficult to work in. However, with noise-cancelling headphones, they might become the most productive team members due to their intense focusing abilities.
- Example #2: A neurodivergent might struggle in a job interview, but if the interview involves a skill test, they would pass and get the job. Because of their focus abilities and attention to detail, neurodivergent people can perform exceptionally well and even make good accountants or record keepers simply because they would love such tedious work compared to non-neurodivergent people.
Lack of Empathy: It is wrong to state that neurodivergent people are not empathetic; their unique understanding of the world gives them better perception powers to understand situations better. It’s just that they might display empathy differently, although it would be more genuine.
Lack of intelligence: Are neurodivergent people unintelligent? Albert Einstein, Marie Curie, Hans Christian Anderson, Bill Gates, Richard Branson, Michael Angelo, Charles Darwin, Nikola Tesla, Elon Musk, Emily Dickinson, and Billy Eilish. Do these examples answer the question?
Can You Become Neurodivergent?
Most forms of neurodivergence have always been a natural part of an individual’s brain development and function. Some may not manifest in childhood but appear as one grows older. Neurodivergence can also occur due to neurological conditions such as brain trauma, injury, stroke, and Alzheimer’s.
How Will I know if I am Neurodivergent?
Being diagnosed with any of the conditions mentioned in this article associated with neurodivergence will make you neurodivergent. However, if you strongly display the symptoms of neurodivergence and have never been diagnosed with any such condition, it is advisable to consult a professional for an assessment. For many people, self-diagnosis is the best way to identify if you are neurodivergent.
What Is It Like to Be Neurodivergent?
No expert can answer what it is like to be neurodivergent simply because every individual is different; thus, every form of neurodivergence is unique and different.
Is There a Cure for Neurodivergence?
Firstly, why would anyone want to be cured of possessing cognitive abilities higher than the average human? If a neurological condition exists causing the neurodivergence, then that is manageable through counseling, therapy, and medication, such as in the case of ADHD. Psychotherapy and counseling will help navigate obstacles while improving on the strengths and abilities of the condition. Neurodivergence itself cannot be prevented, treated, or cured.
Dealing With Neurodivergent People
This is a question that needs to be understood in a broader perspective. Did all the famous neurodivergent people need a support system or others to understand them? Neurodivergent individuals need support and compassion when it involves those with conditions that sometimes can affect their daily lifestyle and mental wellbeing.
New research on the complexities of the human brain will help us change the way we look at neurodivergent people. In the future, autistic people will not be looked upon as those with some disease that needs curing but as people who are simply different and with special abilities. By accepting, understanding, and accommodating the diversity of how different people experience the world, society becomes more compassionate and inclusive, embracing the richness and fascination of neurodivergence.