What is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a psychotic mental disorder and is characterized by behavioral and social abnormalities. People who are suffering from schizophrenia may experience symptoms such as delusion, disorganized speech, hallucinations, a lack of motivation, and trouble with thinking. In other words, schizophrenia affects the way you think, express emotions, actions, and perceive reality compared to a normal person.
However, with the right kind of treatment, this mental disorder can be cured. Having said that, in this article, we will talk about the symptoms, causes, treatments, and many other topics that are related to schizophrenia.
Symptoms of Schizophrenia
When we talk about the symptoms of schizophrenia, we can categorize the symptoms into five distinct categories. With each category, we can observe a different level of schizophrenia. Here are those categories.
- Early Symptoms
- Positive Symptoms
- Negative Symptoms
- Cognitive Symptoms
Early Symptoms
These early symptoms are the first recognizable signs that show in men and women. In men, these symptoms will come up during the late teen years or early 20s. In women, these symptoms will come up during their early 20s and 30s. Besides, this level is known as the prodromal period. The symptoms can last for a few days, weeks, or sometimes years. However, during this period, you cannot spot the symptoms clearly. Early symptoms can include.
- withdrawal from friends, family or other social groups
- Trouble in focus and concentration
- Difficulties during sleeping
- Temper and agitation
- A sudden change in grades or poor academic performance
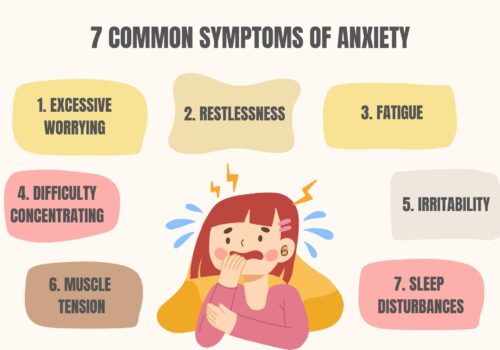
- anxiety
Positive Symptoms
In schizophrenia, positive symptoms reflect an excess or distortion of normal functions. Most people called these symptoms, psychotic symptoms. Having said that, These positive, abnormal symptoms may include:
- Delusions: Delusion refers to false, strange, and mixed beliefs that do not exist in reality and usually involve misinterpretation of perception or experience. For instance, a delusional person might believe that he can hear other people’s thoughts.
- Hallucinations: A hallucination involves seeing and hearing things that do not exist. Hearing voices or auditory hallucinations is the most common form of hallucination that most people suffer from.
- Thought disorder: Thought disorder is a disorganized way of thinking that may result in stopping speech or putting together meaningless words in speaking and writing.
Negative Symptoms
Negative symptoms refer to an absence or lack of normal mental function. They may appear months or year before positive symptoms, they include :
- Appearing to lack of emotion
- Less energy
- Social withdrawal
- Loss of motivation
- Lack of pleasure
- Grooming habits and poor hygiene
Cognitive symptoms
Cognitive symptoms involve trouble with cognitive and mental function These symptoms interfere with the ability to perform routine daily tasks. They include:
- Difficulty in processing information to make decision
- Difficulty in focusing paying attention
- Concentration and Memory problems
Types of Schizophrenia

There are five diverse types of schizophrenia. the subtypes are defined in accordance with most prominent characteristics.
- Paranoid schizophrenia
- Disorganised schizophrenia
- Catatonic schizophrenia
- Undifferentiated schizophrenia
- Residual type schizophrenia
Paranoid Schizophrenia
This is the most common type of Schizophrenia. Those suffering from this schizophrenia begin to show their symptoms during the later part of life. The paranoid type of schizophrenia is marked by thoughts of conspiracy or suspicions such as some is out to harm you or a loved one is cheating on you.
Disorganized schizophrenia
Disorganized schizophrenia is commonly referred to as “hebephrenia” and is characterized by disorganized behavior, speech, and emotional expression. Disorganized schizophrenia is seen most often in teens and young adults between the ages of 15 and 25. People displaying difficulty concentrating thoughts, which manifest in the way they speak, respond to questions with unrelated and illogical answers.
Catatonic Schizophrenia
Catatonic schizophrenia is a rare form of severe mental disorder characterized by disturbance in motor behavior, which many include symptoms like agitation, purposeless movement and in some cases the patient may remain in rigid posture for hours or even days.
Undifferentiated Schizophrenia
In this schizophrenia type, patients symptoms may fluctuate, or may stay stable. Symptoms aren’t enough to classify the patient under any sub type. This disorder does not have any specific symptoms and mostly patients experiencing Delusions, Hallucinations, Disorganized speech or change in behavior.
Residual type schizophrenia
Residual schizophrenia are the less severe form of schizophrenia when positive symptoms of schizophrenia such as delusion, hallucinations, delusional thinking) are not actively displayed in a patient although they will still be displaying negative symptoms (no expression of emotions, strange speech). An individual with residual schizophrenia could be transitioning from an acute phase of schizophrenia to remission or vice versa. Residual schizophrenia is not cyclical and can disappear or reappear at any time
Phases of Schizophrenia
A person that suffers from schizophrenia will show the following three stages. According to the stages, the treatment might vary. Having said that, here are the three main stages of schizophrenia.
Prodromal: The early stage of schizophrenia usually involves non-specific symptoms. Symptoms of Prodromal schizophrenia include lack of nervousness, anxiety, social withdrawal, lack of motivation, sleep problems
Active: Active stage involves noticeable psychotic symptoms. During this stage, a patient might show elevated symptoms such as hallucinations, psychosis, suspiciousness, and delusions. If not treated correctly, the symptoms of the active stage might last for weeks or months. So, the illness should be treated immediately.
Residual: In residual schizophrenia, a person experiences less severe symptoms, People may experience negative symptoms, such as a lack of motivation, low energy, or social withdrawal.
Causes of Schizophrenia
Even though there is no exact source of schizophrenia, this chronic brain disorder is a real illness like diabetes and cancer. However, the researchers have discovered several other factors that can increase the chances of getting schizophrenia. In this section, we are going to discuss about those causes of schizophrenia.
Genetics
One of the major risk factors for schizophrenia may be genes. The researchers believe that the genetic vulnerability and environmental factors both act in combination so as to result in diagnosis of schizophrenia
Brain Chemistry
Our brain produces a chemical known as neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters can control the nerve cell circuit. And nerve cells affect the behaviors and thinking of a person. When your brain produces a small number of neurotransmitters, you might get schizophrenia.
Brain Abnormality
If someone has an abnormal brain structure, they might suffer from schizophrenia. However, this is not always true. That means this theory does not apply to all schizophrenia patients.
Environment
A person’s surroundings can cause schizophrenia. For instance, viral infection, highly stressful situations, and marijuana can trigger schizophrenia. Besides, we can see symptoms of schizophrenia during someone’s physical and hormonal changes.
How to Treat Schizophrenia
As you already know, most people that have schizophrenia cannot be recognized until the second phase. However, at the second phase, you might have to start the treatment process. Here are some of the treatments that you can follow easily.
Medicines
You already know that the number of neurotransmitters your brain produces has a profound effect on schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications are the most commonly prescribed drugs, that control the symptoms by releasing the number of neurotransmitters in your brain. The goal of treatment with antipsychotic medications is to effectively manage signs and symptoms at the lowest possible dose. People with schizophrenia may be reluctant to take medication as schizophrenia medications may cause serious side effects
Side Effects of Schizophrenia Medicines
There are some of the common side effects of antipsychotic medications that includes:
- Drowsiness
- Restlessness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Skin rash
- Menstrual problems
- Sexual Problems
Psychosocial Treatment for Schizophrenia
While medication is necessary for schizophrenia treatment, it does not offer a complete solution. People with schizophrenia also need psycho-social treatments to help them cope with their illness, and become more independent. People who receive psycho-social treatment for schizophrenia are more likely to take their medication regularly and avoid relapse and hospitalization.
Hospitalization
If a person shows extreme symptoms, it might be time for hospitalization. Remember, a severe level of schizophrenia patients can be a danger to themselves and others. So, hospitalization might be the only option.
Final Takeaway
Schizophrenia can be a dangerous mental disorder if you do not treat the illness properly. With the correct medication and therapy, schizophrenia can be cured properly. However, it might take some time. On the other hand, checking your family roots can be vital. It will give you a good idea about your chances of getting schizophrenia.
References:
- https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia
- https://www.webmd.com/schizophrenia/mental-health-schizophrenia
- https://www.healthline.com/health/mental-health/phases-of-schizophrenia#outlook
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org/what-are-the-4-types-of-schizophrenia-and-how-can-they-affect-you/
- https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/schizophrenia/what-is-schizophrenia
- https://www.onhealth.com/content/1/schizophrenia_treatment
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schizophrenia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354443