Dealing with the aftermath of a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) can be overwhelming and isolating for both the person affected and their loved ones. Without a proper support system and medical attention, it can be challenging to cope with the physical, cognitive, and emotional problems that arise from a TBI, especially mental health disorders.
Traumatic brain injuries are known to have long-lasting impacts on a person’s mental health and wellness. However, there are a variety of promising programs and treatments out there that can be customized to help those with TBI navigate the many challenges that come with this type of injury.
In this piece, we’ll delve into the various types of mental health support options that are available for TBI sufferers and their families. These resources can play a key role in aiding recovery, building resilience, and promoting vitality after experiencing such a life-altering event.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury
A TBI occurs when a blow or jolt to the head disrupts normal brain functioning. It can result in various physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral impairments. It’s crucial to understand the causes and effects of TBI and its connection to certain mental conditions.
The causes of a TBI can range from falls to motor vehicle accidents, sports injuries, or even violent assaults. The severity of the injury can vary from mild to severe, depending on the force and duration of the impact. Common physical symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea, and sensory disturbances. Cognitive difficulties such as memory loss, attention deficits, and problem-solving difficulties may also arise in some cases.
In addition to the physical and cognitive challenges, TBIs are often associated with mental health issues. Survivors may experience depression, anxiety, PTSD, or adjustment disorders, which can significantly affect their emotional state and relationships.
Getting help and collaborating with a medical professional is crucial for those who’ve suffered a TBI. Professional guidance can assist survivors and their loved ones in understanding and tackling the unique hurdles that may arise post-injury.
Mental Health Challenges Associated with TBI
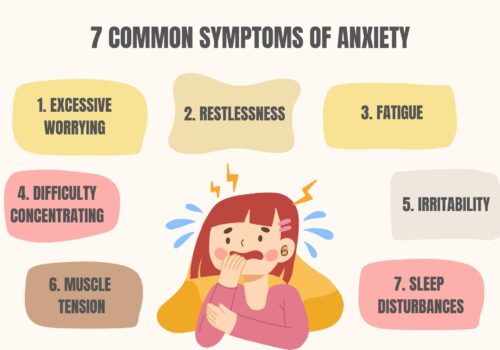
Dealing with a traumatic brain injury often entails managing a host of mental health challenges. Depression is one of the most common struggles, as people with a TBI are more prone to feeling down and disinterested in things they used to enjoy. The physical, emotional, and cognitive changes can all precipitate feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest. Anxiety is another fairly common challenge, leading to increased worry, restlessness, and uneasiness. Managing stress and adapting to new situations can be especially difficult for them.
PTSD can develop alongside a TBI, as the traumatic event that caused the injury may trigger distressing memories and nightmares. The emotional toll of the injury, along with cognitive difficulties, can make it challenging for individuals to process and cope with the trauma, increasing the risk of developing PTSD.
Schizophrenia and other psychotic spectrum disorders are less frequent but equally significant mental health challenges associated with TBI. The brain’s functioning can be disrupted by the injury, resulting in hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Those with a TBI may display symptoms resembling those of primary psychotic disorders.
Additionally, there is a heightened susceptibility to substance use disorders following a TBI. The injury can elevate the risk of substance abuse, as people may resort to drugs or alcohol for solace. This, in turn, exacerbates cognitive impairment and impedes the healing journey.
Mental Health Support Services
People with traumatic brain injuries may experience a range of challenging mental health symptoms that necessitate proper assistance. Let’s explore the plethora of treatment support services already in place, ready to offer the relief you deserve.
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a popular treatment option for a wide variety mental health issues. It works by helping individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors, leading to improved coping skills. CBT has been proven effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions, particularly those stemming from traumatic brain injuries.
2. Counseling
Seeking counseling services can provide invaluable support and guidance during challenging times. Whether you prefer one-on-one sessions, group therapy, or family counseling, there are options available to suit your individual needs. These services aim to facilitate healing and enhance emotional well-being by creating a nurturing and understanding environment where you can express yourself freely.
3. Support Groups
Some organizations offer support groups specifically for individuals with TBIs and associated mental health symptoms. These groups provide people with the opportunity to connect with others facing similar challenges, exchange experiences, and receive social and emotional support.
Coping and Recovery Strategies
Navigating the aftermath of a traumatic brain injury requires a personalized approach to recovery, empowering individuals to reclaim their autonomy and live life to the fullest. Here are a few strategies to consider when embarking on the recovery journey:
- Focusing on accomplishments: Recognizing and celebrating small milestones can help boost self-esteem and motivate you to continue your recovery journey. Recognizing even small advancements is crucial. Celebrate each small step as a triumph on your journey forward.
- Challenging unhelpful thoughts: While recovering from a brain injury, people may experience negative thinking patterns that hinder their progress. Challenge those negative thoughts and swap them out for positivity to boost your mental strength and resilience.
- Rediscovering self-value: The journey of finding oneself again after a brain injury can bring about a new sense of purpose and identity. Participating in activities that encourage personal development can aid in building self-esteem and reshaping self-perception.
- Engaging in psychotherapy: Therapists can provide incredible guidance and support in navigating the challenges that arise during the recovery process. They’re like your personal cheerleaders, helping you set goals that are both achievable and exciting, keeping you encouraged and ready to tackle anything that comes your way.
Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
After a traumatic brain injury, it’s not just the body that can be affected, but the mind too. Mental health issues are like unexpected guests crashing the recovery party. Overcoming the stigma surrounding mental health can be a challenging obstacle for many, preventing them from seeking the necessary support they deserve. But breaking free from this stigma is crucial for putting your mental well-being first.
In an ideal world, societies would prioritize promoting understanding and acceptance of mental health issues following a brain injury. By sparking education and spreading awareness, we can break down barriers and shatter stereotypes with targeted initiatives and engaging campaigns. By spreading awareness about the connection between brain injuries and mental health, we can break down stigma and make a positive impact.
The next step is seeking professional help. Mental health professionals have the expertise to assess and provide appropriate treatment for the various mental health problems that may arise after a brain injury.
Self-care is essential and should always be prioritized. Nurturing your mind is just as vital as caring for your body. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and self-soothing is beneficial for reducing the impact of mental health problems after a brain injury. This can include practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, and seeking healthy coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
If you or a loved one is affected by a traumatic brain injury, know that there is help available. From counseling to support groups and specialized therapies, there are resources to guide you through the challenges. Even in the face of severe injuries, you are not alone on this journey. Embrace the support available to you and reach out for the help you deserve. It’s more than possible to thrive after a traumatic brain injury with proper care and support.