Understanding personality disorders is essential for a better grasp of human behavior. These disorders, affecting millions of people worldwide, can have a significant impact on individuals’ lives and the lives of those around them. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various types of personality disorders, shedding light on their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
From narcissistic personality disorder to borderline personality disorder, this article provides insights into seven different types of personality disorders. Each disorder is explored in depth, presenting a clear picture of the distinctive traits and behaviors associated with it. We’ll uncover how these disorders affect relationships, work life, and overall well-being and offer practical tips for managing and coping with them.
Understanding Personality Disorders
Personality disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by long-standing patterns of behavior, thoughts, and emotions that deviate from societal norms. These patterns usually manifest in adolescence or early adulthood and continue throughout a person’s life. They can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function, maintain healthy relationships, and experience overall well-being.
There are several clusters of personality disorders, each with its own unique set of characteristics. Understanding these clusters is crucial for differentiating between the various types of personality disorders and developing appropriate treatment plans.
The Different Clusters of Personality Disorders
Personality disorders are categorized into three clusters: Cluster A, Cluster B, and Cluster C. Each cluster represents a distinct set of personality disorders, each with its own specific traits and behaviors. Let’s explore each cluster and the personality disorders within them in more detail.
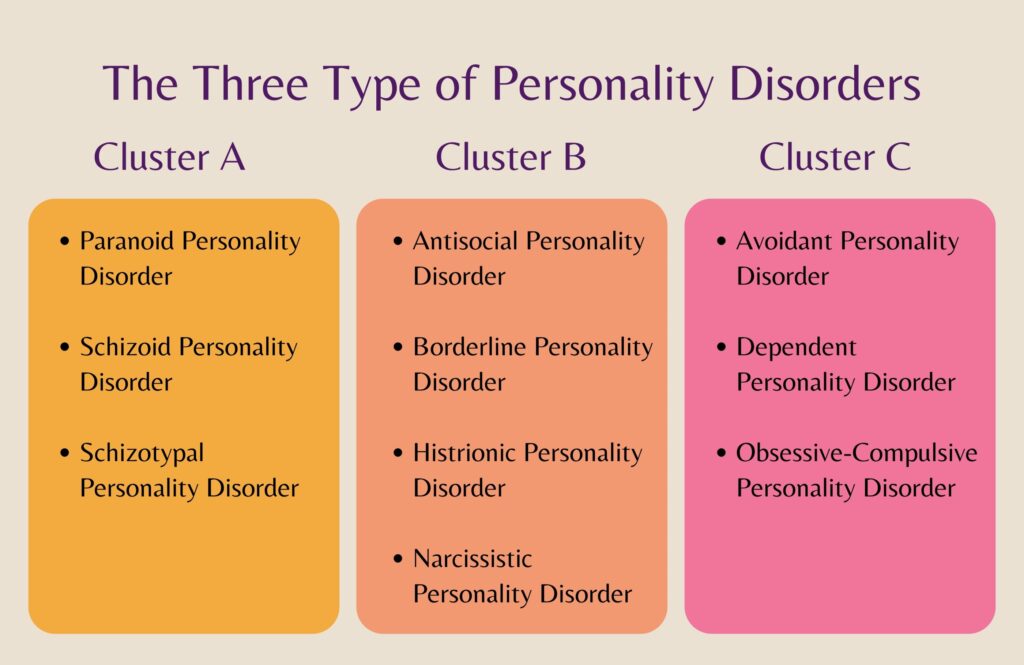
Cluster A: Paranoid, Schizoid, and Schizotypal Personality Disorders
1. Paranoid Personality Disorder
People with paranoid personality disorder exhibit a pervasive distrust and suspicion of others. They often interpret innocent actions as malevolent and doubt the loyalty and trustworthiness of those around them. This unwarranted distrust can strain relationships and hinder personal and professional growth.
2. Schizoid Personality Disorder
Schizoid personality disorder is characterized by a lack of interest in social interactions and a limited range of emotional expression. Individuals with this disorder often prefer solitude and struggle with forming close relationships. They may appear aloof, detached, and indifferent to others’ emotions, causing interpersonal difficulties.
3. Schizotypal Personality Disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder is characterized by odd beliefs, behaviors, and perceptions. People with this disorder may have eccentric thoughts, exhibit peculiar speech patterns, and experience difficulties with social interactions. While they may desire social connections, their unusual behaviors can make it challenging to form and maintain relationships.
Cluster B: Antisocial, Borderline, Histrionic, and Narcissistic Personality Disorders
1. Antisocial Personality Disorder
Antisocial personality disorder is characterized by a disregard for others’ rights, lack of empathy, and a tendency towards manipulative and exploitative behaviors. People with this disorder often engage in criminal activities, show no remorse for their actions, and have difficulty forming and maintaining relationships.
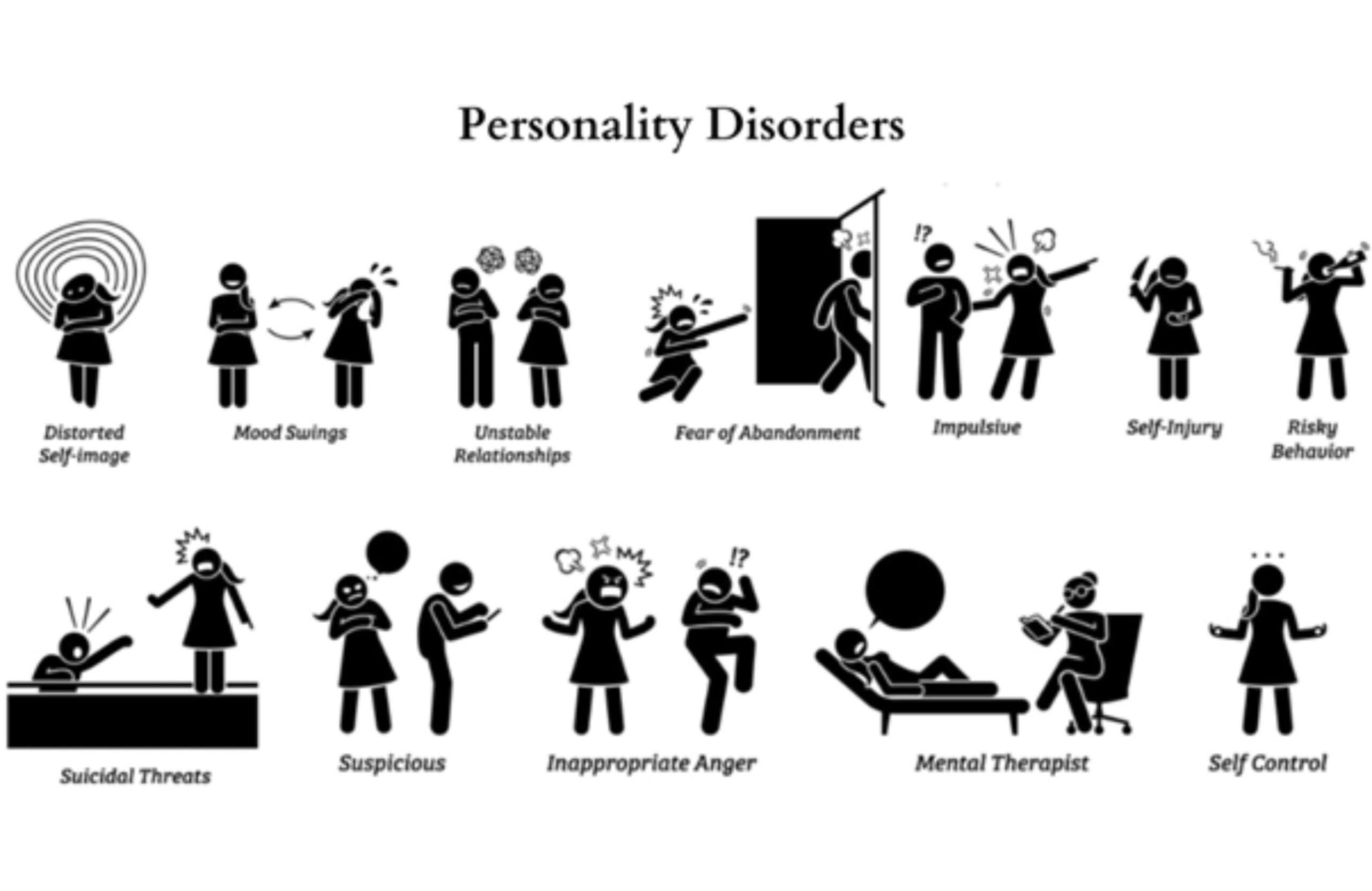
2. Borderline Personality Disorder
A borderline personality disorder is characterized by intense mood swings, unstable self-image, and impulsive behavior. Individuals with this disorder often fear abandonment and may engage in self-destructive behaviors, such as self-harm or substance abuse. They may also struggle with maintaining stable relationships due to their emotional volatility.
3. Histrionic Personality Disorder
Histrionic personality disorder is characterized by attention-seeking behavior, excessive emotions, and a need for constant validation and approval. People with this disorder often crave attention and may engage in dramatic or provocative behaviors to gain it. Their intense emotions and constant need for reassurance can strain relationships and lead to feelings of emptiness.
4. Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Narcissistic personality disorder is characterized by an inflated sense of self-importance, a need for admiration, and a lack of empathy for others. Individuals with this disorder often have a grandiose view of themselves and believe they are superior to others. They may exploit others for personal gain and struggle with maintaining healthy relationships due to their self-centeredness.
Cluster C: Avoidant, Dependent, and Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorders
1. Avoidant Personality Disorder
Avoidant personality disorder is characterized by extreme social anxiety, fear of rejection, and feelings of inadequacy. People with this disorder often avoid social interactions and may isolate themselves to avoid potential criticism or embarrassment. Their fear of rejection can hinder their ability to form and maintain relationships.
2. Dependent Personality Disorder
Dependent personality disorder is characterized by a pervasive need to be taken care of by others. Individuals with this disorder often rely heavily on others for decision-making, reassurance, and support. They may fear being alone and struggle with asserting themselves in relationships, leading to feelings of helplessness and reliance on others.
3. Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder
Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder is characterized by a preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and control. People with this disorder often strive for perfection, leading to rigid and inflexible behaviors. Their obsession with details and need for control can strain relationships and hinder their ability to adapt to change.
Causes and Risk Factors of Personality Disorders
Personality disorders involve persistent deviations from societal norms in behavior, thoughts, and emotions. Apart from specific types, there are “other specified” and “unspecified” categories for cases not fitting a precise diagnosis. Examples include Personality Disorder Trait Specified (PDTS) which focuses on problematic traits like intense anger, and Unspecified Personality Disorders which have symptoms that do not align with a specific disorder. Recognizing these categories is crucial for understanding the intricate nature of personality disorders, emphasizing the need for support and treatment even if a specific diagnosis isn’t met.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Personality Disorders
- Multifaceted Origins: Personality disorders result from a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and social factors. While a genetic predisposition is evident, it does not solely determine the development of these disorders.
- Environmental Impact: Childhood experiences, such as abuse or inconsistent parenting, significantly influence personality development. Traumatic events and adverse experiences increase vulnerability to personality disorders by shaping an individual’s coping mechanisms and worldview.
- Social Influences: Cultural norms and societal expectations also play a role. Different standards for acceptable behavior in various cultures can impact the perception and diagnosis of personality disorders. Understanding these diverse factors is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment strategies.
Living With a Personality Disorder: Coping Mechanisms and Support
Diagnosing Personality Disorders:
- Challenging due to complex symptoms and overlap with other mental health conditions.
- Specific criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) are used for an accurate diagnosis.
- DSM-5 classifies personality disorders into three clusters: Cluster A (odd or eccentric behavior), Cluster B (dramatic, emotional, or erratic behavior), and Cluster C (anxious or fearful behavior).
Treatment Approach:
- Involves a multidisciplinary approach.
- It combines therapy, medication, and support services.
- Psychotherapy, including dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), is commonly used. You need to understand the Pros and Cons of DBT Therapy and CBT Therapy, which will be helpful for you who are undergoing Personality Disorder.
- Aims to help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms, improve interpersonal skills, and manage emotions.
- Medication may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms (e.g., depression, anxiety, impulsivity).
- Medication alone is not sufficient and is usually used in conjunction with therapy.
- Support services, such as support groups or community programs, play a crucial role in providing a safe and understanding environment.
Support Services:
- Offer a platform for individuals to share their experiences, learn from others, and receive ongoing support.
- Include support groups and community programs.
Individualized Treatment:
- Treatment approaches may vary based on the specific personality disorder.
- A tailored treatment plan considers individual symptoms, goals, and circumstances.
- Essential for successful management of personality disorders.
Conclusion: Breaking the Stigma and Seeking Help for Personality Disorders
Living with a personality disorder can be challenging, but effective coping mechanisms and support systems can make a significant difference. Self-care, including mindfulness and hobbies, helps reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, proper sleep, and a balanced diet contributes to overall mental health.
Building a strong support system is crucial. Surrounding oneself with understanding friends, family, or support groups provides validation and encouragement during difficult times. These relationships also offer practical help and guidance.
Seeking professional help is vital. Mental health professionals can provide guidance, support, and therapy to navigate the challenges associated with personality disorders. Regular therapy sessions offer a safe space for exploring emotions, developing coping strategies, and working toward personal growth.